Crush Syndrome

When a person is crushed by a heavy object, such as a building collapse or a car accident, they develop crush syndrome. Symptoms include muscle damage, kidney failure, and shock, and the condition can be life-threatening if untreated. We will provide a comprehensive guide to understanding crush syndrome, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Causes of Crush Syndrome
The crush syndrome occurs when a person’s body is compressed for a prolonged period of time by a heavy object. As a result of this compression, toxins are released into the bloodstream, causing damage to muscles and tissues. Other factors, such as natural disasters, industrial accidents, or military combat, can also cause crush syndrome.
Symptoms of Crush Syndrome
There can be a variety of symptoms associated with crush syndrome depending on the severity of the injury, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Swelling and pain in the muscles
- The affected area receives less blood flow
- Elevated heart rate
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion and disorientation
- Low blood pressure
- Kidney failure
- Shock
Crush Syndrome Treatment
In the event of crush syndrome, treatment should be begun right away. Some of the most common treatments for crush syndrome include:
- Objects that are crushing should be removed immediately
- Management and care of wounds
- Replacement of fluids to prevent dehydration and shock
- Pain management
- Using dialysis to treat kidney failure
Furthermore, adequate medical facilities and personnel are necessary to provide adequate care to those affected.
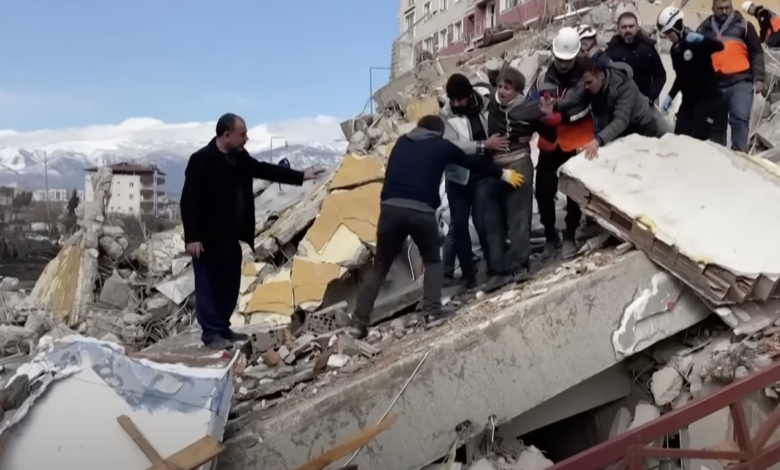
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes and hurricanes, can cause massive damage to buildings and infrastructure. Crush syndrome occurs when people become trapped beneath the rubble of collapsed buildings. Crush syndrome, also known as traumatic rhabdomyolysis, the release of muscle contents, such as myoglobin, can cause kidney damage and other organ failures, making this a dangerous and life-threatening condition.
When a building collapses, the pressure from the collapsed material can compress and crush a person’s limbs or other parts of their body, resulting in muscle injury and muscle contents being released into the bloodstream. To prevent serious long-term health complications, rescue personnel should identify and treat victims of crush syndrome as soon as possible. In most cases, rehydration and medication are administered to prevent kidney damage, as well as close monitoring of the patient’s medical condition.
The risk of developing medical conditions such as hypothermia, dehydration, and infections is also high for people trapped under rubble for an extended period of time.
Crush Syndrome Prevention
If you are working with heavy machinery or in a situation where there is a high risk of crushing injury, you should follow safety guidelines to avoid crush syndrome. Be sure to wear protective clothing and equipment, follow proper lifting techniques, and remain aware of your surroundings at all times.
After a person has been crushed by a heavy object, they can develop crush syndrome, a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Crush syndrome can be identified and treated using properly trained rescue teams, the right equipment, and clear protocols.To prevent and manage crush syndrome, it is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know seems to be suffering from crush syndrome.